
Adaptive vs Maladaptive Behaviors in ABA
Think of the movie “Good Will Hunting’’, where Will Hunting, a brilliant young man, contended with lots of potential. On one hand, he is blessed with an acute mind – an adaptive trait that has opened doors of opportunities for him. On the other hand, he has maladaptive behaviors — anger, mistrust, and self-sabotage— that keep him in the trap of self-doubt and missed opportunities. However, Prof. Lambeau transformed his life and changed Will’s maladaptive behaviors into adaptive traits.
In the context of Applied Behavioral Analysis, an ABA therapist does the same as Prof. Lambeau did. They identify the adaptive and maladaptive behaviors and then shape these behaviors carefully.
What are adaptive and maladaptive behaviors, and how do they differ from each other? Let’s find out in this article.
But before heading into improving behaviors, it is crucial to understand why certain behavior occurs. The therapist focuses on the “why” behind the behaviors or the function of behaviors, as this is the foundational step for creating effective interventions in ABA therapy.
Table of Contents
Understanding Adaptive Behaviors
You can understand adaptive behaviors as a set of actions and responses that help a person live in an environment effectively. Adaptive behaviors such as conceptual skills, social skills, and practical skills are also crucial to meet the demands of everyday life. If a person has well-developed adaptive behaviors, he can easily adjust to new challenges, solve problems, and achieve his goals in a constructive and beneficial manner.
Characteristics
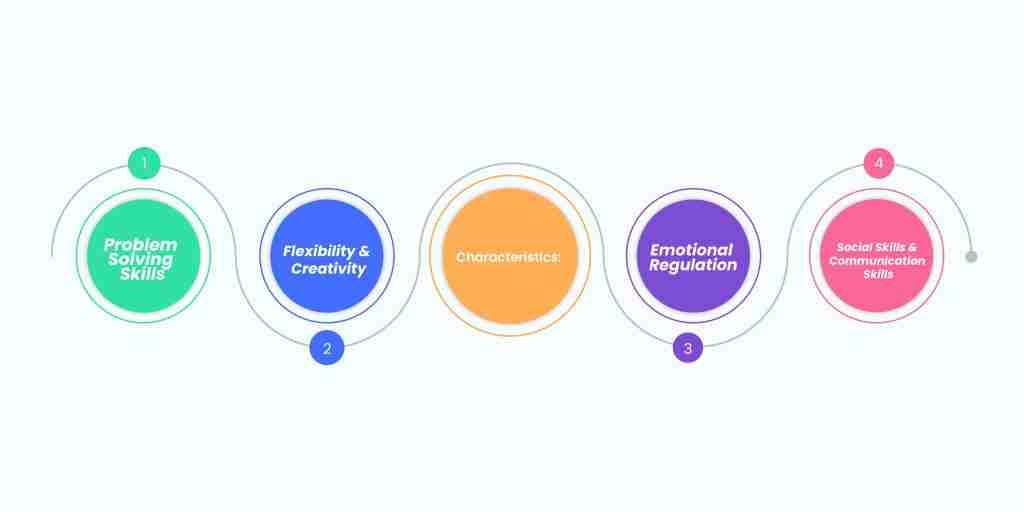
- Problem-solving skills
Individuals with adaptive behaviors can easily identify problems in their lives and find effective solutions for them. Instead of taking things to their heads, they take help from critical thinking and resourcefulness, break down complex issues into manageable steps, and solve the problem.
- Flexibility and creativity
A person with adaptive behavior must know how to adjust to transitioning and challenging environments and spaces. Even if the situation is not what the person planned, such individuals think out of the box and find solutions to achieve the objectives in unpleasant situations as well.
- Emotional regulation
Emotional regulation is one of the keystones of adaptive behaviors. It helps individuals manage their emotions regularly. This involves understanding and recognizing other’s emotions, controlling negative emotions, and responding to situations with appropriate emotions.
- Social skills and communication skills
Social skills and communication skills are considered the characteristic traits of adaptive behaviors as they help in building and maintaining healthy social connections. This includes the ability to efficiently understand the second person’s point of view and effectively communicate your thoughts and ideas.
Examples
- A person learning braille even after losing his vision.
- A person asks for help when needed.
- A person who moves to a new country adapts to their cultural norms.
Understanding Maladaptive Behaviors
Maladaptive behaviors are those traits or actions that inhibit the ability of individuals to bring changes in themselves when they encounter challenges, stressors, or a transition in the environment. Such people consider these acts a solution or a way to relieve themselves, but in reality, they are just for short-term relief. In the long term, maladaptive behaviors pose a lot of damage to the relationships and emotional, mental, and physical health of the person.
Characteristics
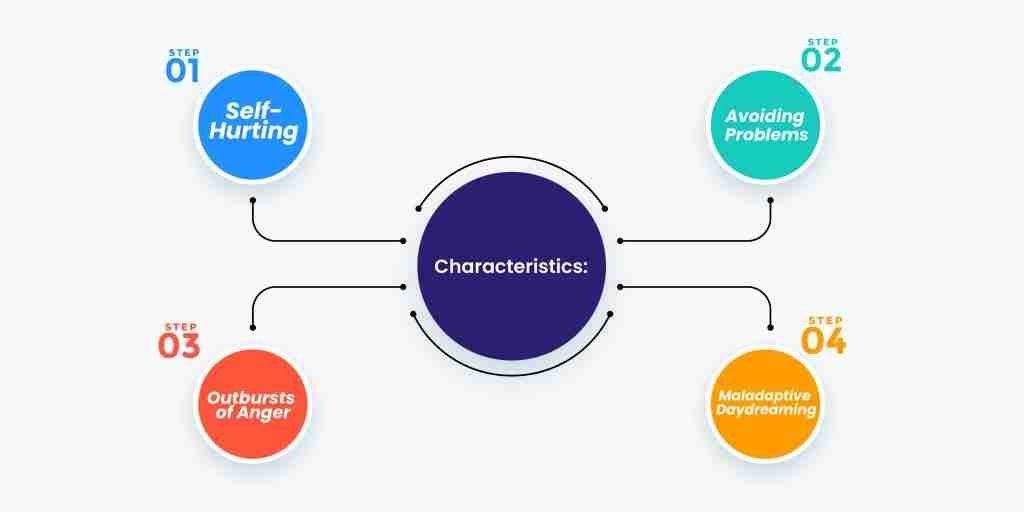
- Self-hurting
Self-hurting is one of the most disruptive behaviors that people usually do to cope with distress. They find it soothing and a way to lower their anger levels or stress levels.
- Avoiding problems
A key trait of maladaptive behavior is avoiding problems and escaping from them. As such, people don’t know how to face and regulate any situation; they find escape as an option and engage themselves in other activities as a distraction. This approach helps them in the short term, but with time, avoiding the situations exacerbates the issue.
- Outbursts of anger
People with maladaptive traits don’t know how to respond to stressors and challenges. As a result, they have frequent outbursts of anger that affect their relationships and their own mental health as well.
- Maladaptive daydreaming
Maladaptive daydreaming refers to immersing yourself in a fantasy world to escape from real-life challenges and situations. While daydreaming possesses no harm and even nurtures creativity, maladaptive daydreaming can be worse as it affects the ability of the person to function in the real world.
Examples
- A person striking his head on the wall to manage the stress.
- A person screaming and yelling over an unpleasant situation.
- A child with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) throws tantrums because of the sensory overload caused due to lights and noise.
Role of ABA in Addressing Maladaptive Behaviors

Step 1: Assessment and understanding of the function of maladaptive behaviors
The first and foremost step of ABA therapy is to understand ‘why this behavior occurs.’ This is very crucial, specifically while dealing with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) children, as they often face difficulties in expressing their needs and regulating their emotions.
This is why an ABA therapist starts by identifying the function of maladaptive behaviors. He focuses on whether the certain behavior is because the child is trying to seek attention or to escape from the situation. As ASD children are more likely to be aggressive and engage in self-harm activities, understanding the underlying reason behind their behaviors is crucial.
Step 2: Implication of intervention strategies
Once the ABA therapist figures out the function of behavior by functional behavior assessment (FBA), behavioral analysis, interviews, and questionnaires, he develops interventions accordingly. These interventions aim to teach autistic children alternative adaptive behaviors for their maladaptive traits. Some of the targeted intervention strategies are:
- Replacement behaviors
It is one of the most commonly used strategies in ABA, where the therapist teaches an alternative to maladaptive behavior. For example, if a child makes lots of noise in the classroom to get noticed, he may be trained to use any specific sign to get attention.
- Functional communication training
Usually, children with autism struggle with communication, due to which they can’t communicate their needs, which leads to the development of maladaptive behaviors. ABA therapy gives functional communication training that teaches them how to communicate with gestures, signs, and communication devices.
- Skill acquisition programs
Skill acquisition programs in ABA are designed in such a way that they teach the children the necessary skills to live their lives independently and effectively. It also focuses on reducing the reliance of the child on maladaptive coping behaviors and provides them with positive soothing and coping solutions. For example, teaching children to breathe in and out in stressful conditions instead of hurting themselves helps them manage the stress without causing any harm.
Conclusion
So, ABA therapy is a great help specifically for children with autism spectrum disorder, replacing maladaptive behaviors with adaptive ones.
Read About: Behavioral Insights into the Four Core Functions


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.